Tech
The Complete Guide to Surface Roughness and How it Affects Your Product

Surface roughness, also known as surface finish, is a measure of the texture of a surface. It is typically measured by means of a profilometer, which scans the surface with a stylus that feels the contours of the surface. The resulting profile is then analyzed to calculate the roughness parameters. In this blog post, we will provide a complete guide to surface roughness and what factors influence it. We will also show how you can use surface roughness to improve the quality of your products. Read on to learn more!
Factors affecting surface roughness
There are many factors that can affect surface roughness, including manufacturing process, material properties, and environmental factors.
-
Manufacturing process
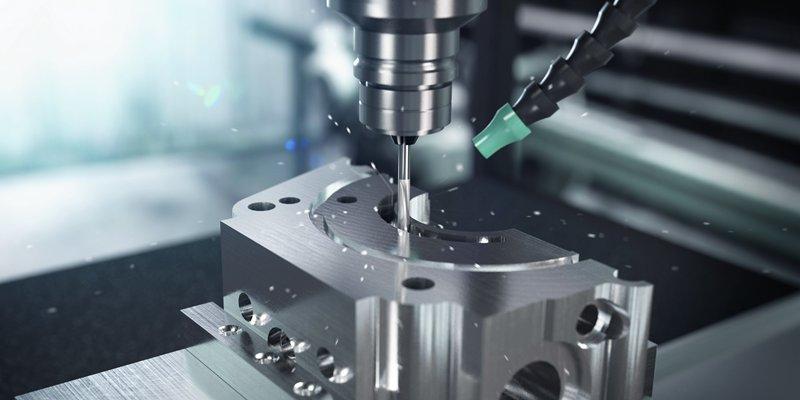
The type of manufacturing process used has a direct impact on surface roughness. The main types of manufacturing processes are classified as either subtractive or additive. Subtractive processes include machining operations such as turning, milling, and grinding. In these processes, material is removed from the workpiece to achieve the desired shape and surface finish.
Additive processes include 3D printing and other processes where material is added to the workpiece to achieve the desired shape. The main difference between these two types of processes is that subtractive processes typically result in a rougher surface finish, while additive processes can produce a much smoother surface finish. For example, machining operations tend to produce surfaces with higher roughness values than casting or forming processes.
When choosing a manufacturing process for a particular application, it is important to consider the surface roughness that will be achieved. For many applications, a smooth surface finish is desired in order to reduce friction and wear. In other cases, a rougher surface finish may be desirable for improved grip or aesthetics.
-
Material properties
Surface roughness can also be affected by the material properties of the workpiece. Softer materials tend to have a rougher surface, while harder materials tend to have a smoother surface. The type of material also affects surface roughness. Metals tend to have a smoother surface than plastics or composites.
The grain size of the material can also affect the surface roughness. In general, smaller grain sizes result in smoother surfaces, while larger grain sizes can lead to more textured surfaces. The heat treatment of the material can also influence the surface roughness. For example, softer materials that have been annealed tend to produce smoother surfaces, while harder materials that have been quenched tend to produce more textured surfaces.
Surface roughness can also be affected by the manufacturing process. Surface roughness is affected by the tooling, cutting speed, feed rate, and depth of cut. The surface roughness of a workpiece can also be affected by heat treatment or surface treatments.
Understanding how the material properties of a workpiece affect the surface roughness can help predict the outcome of machining operations and choose the most appropriate methods for achieving the desired results.
-
Environmental conditions
The surface of any metal can become rougher over time due to a variety of environmental factors. For instance, exposure to high temperatures can cause the metal to expand and contract, resulting in uneven surfaces. Similarly, humidity can cause water droplets to form on the metal’s surface, leading to an uneven texture. Moreover, dust and other particles can accumulate on the metal over time, causing it to become dull and scratched. In extreme cases, such as when the metal is exposed to strong chemicals or saltwater, the surface can become corroded. As a result, it is important to take environmental factors into account when choosing a metal for a particular application.
How does surface roughness affect the performance of a surface
Surface roughness is a very important factor that can affect the performance of a surface. Surface roughness can cause problems such as friction, wear, and vibration. It can also affect the ability of a surface to resist corrosion and abrasion.
Surface roughness can affect the performance of a surface in several ways. For example, a smooth surface may be more resistant to wear and tear than a rougher surface. In addition, a smooth surface may be less likely to harbor bacteria or other contaminants.
Finally, surface roughness can also affect the way light reflects off of a surface, which can impact optical properties such as transparency and reflectivity. A rougher surface will often scatter light in multiple directions, while a smoother surface will tend to reflect light in a single direction. This property can be exploited in applications such as solar panels or Reflective Insulation Material (RIM).
Consequently, understanding how surface roughness affects the performance of a material is important for applications ranging from engineering to optometry.
In engineering, a rougher surface usually has more friction, which can be beneficial or detrimental depending on the application. For example, a rougher surface will usually create more drag, which can be desirable in applications such as brakes or tires. However, in other applications such as bearings or pumps, a smoother surface is often preferable in order to reduce friction. In addition, surface roughness can also affect the ability of a surface to reflect light or heat.
Ultimately, the effect of surface roughness on the performance of a surface depends on the specific application.
Conclusion
Surface roughness is a critical parameter in many engineering applications, yet its measurement is fraught with difficulties. Synthetic materials such as metals and plastics can be manufactured to very tight tolerances, so their surfaces are typically quite smooth. Natural materials, on the other hand, are often less uniform in their surface roughness. For example, stone surfaces can be quite rough, while wood surfaces can vary widely in their level of smoothness. As a result, accurately measuring surface roughness can be a challenge.
There are a number of different methods that can be used to determine the roughness of a surface, but each has its own advantages and disadvantages. The choice of method will depend on the particular application and the desired accuracy of the measurement. With advances in technology, it is likely that more accurate and reliable methods of measuring surface roughness will be developed in the future.
-
Blog1 year ago
MyCSULB: Login to CSULB Student and Employee Portal – MyCSULB 2023
-
Android App3 years ago
Cqatest App What is It
-
Android1 year ago
What Is content://com.android.browser.home/ All About in 2023? Set Up content com android browser home
-
Software2 years ago
A Guide For Better Cybersecurity & Data Protection For Your Devices
-
Latest News2 years ago
Soap2day Similar Sites And Alternatives To Watch Free Movies
-
Android2 years ago
What is OMACP And How To Remove It? Easy Guide OMACP 2022
-
Android3 years ago
What is org.codeaurora.snapcam?
-
Business2 years ago
Know Your Business (KYB) Process – Critical Component For Partnerships